Preț Measurable Data Token

Limitarea răspunderii
OKX nu furnizează recomandări privind investițiile sau activele. Trebuie să analizați cu atenție dacă să tranzacționați sau să dețineți activele digitale prin prisma stării dvs. financiare. Consultați-vă cu un profesionist în domeniul juridic / fiscal / de investiții pentru întrebări despre circumstanțele dumneavoastră specifice. Pentru detalii suplimentare, consultați Condițiile de utilizare și Avertizarea de risc. Prin utilizarea paginii web terțe („TPW”), acceptați că orice utilizare a unei TPW va fi supusă oricăror și guvernată de orice condiții pentru TPW. Exceptând mențiunile exprese în scris, OKX și afiliații săi („OKX”) nu sunt în niciun fel asociați cu proprietarul sau operatorul TPW. Sunteți de acord că OKX nu este responsabilă sau răspunzătoare pentru nicio pierdere, daună și orice alte consecințe care decurg din utilizarea de către dumneavoastră a unei TPW. Țineți cont că utilizarea TPW poate duce la pierderea sau diminuarea activelor dumneavoastră. Este posibil ca produsul să nu fie disponibil în toate jurisdicțiile.
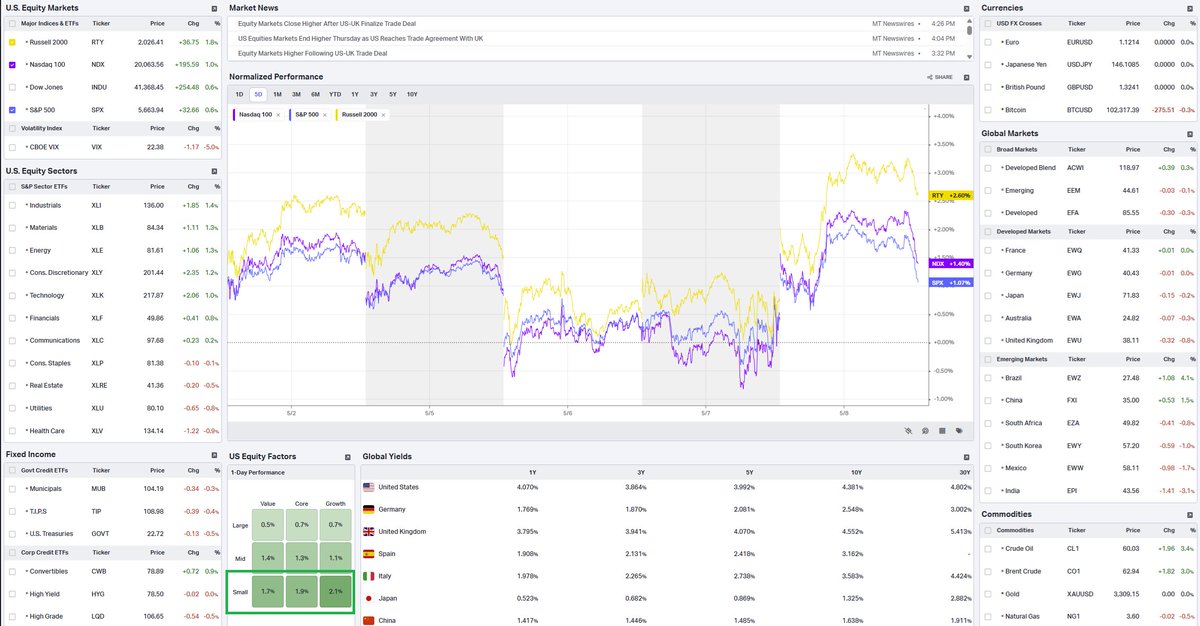
Informații de piață despre Measurable Data Token
Capitalizare de piață = Ofertă în circulație x Ultimul preț

Flux Measurable Data Token










Calculator MDT


Performanța prețului Measurable Data Token în USD
Conversii Measurable Data Token populare
| 1 MDT în USD | 0,020360 $ |
| 1 MDT în EUR | 0,017779 € |
| 1 MDT în PHP | 1,1330 ₱ |
| 1 MDT în IDR | 330,95 Rp |
| 1 MDT în GBP | 0,014994 £ |
| 1 MDT în CAD | 0,027834 $ |
| 1 MDT în AED | 0,074782 AED |
| 1 MDT în VND | 530,90 ₫ |
Despre Measurable Data Token (MDT)
- Pagina web oficială
- White paper
- Github
- Explorator bloc
Întrebări frecvente Measurable Data Token
Measurable Data Token este o piață de date descentralizată, alimentată de blockchain, care se ocupă de date anonime și asigură confidențialitatea. Conectează cumpărătorii și vânzătorii într-un mod imuabil și inviolabil, alimentat de contracte inteligente și tokenul său nativ MDT.
Measurable Data Token permite companiilor să se conecteze anonim cu vânzătorii de date, permițându-le să ofere tot ce pot la prețul corect. Ecosistemul are o aplicație mobilă RewardMe, care permite integrarea fără probleme a utilizatorilor.
Cumpărați cu ușurință tokeni MDT pe platforma de criptomonede OKX. Terminalul de tranzacționare la vedere al OKX oferă perechea de tranzacționare MDT/USDT.
De asemenea, puteți schimba criptomonedele existente, inclusiv XRP (XRP), Cardano (ADA), Solana (SOL) și Chainlink (LINK), pentru MDT cu zero taxe și fără alunecare de preț prin utilizarea OKX Convert.
Raportare privind gazele cu efect de seră
Calculator MDT













